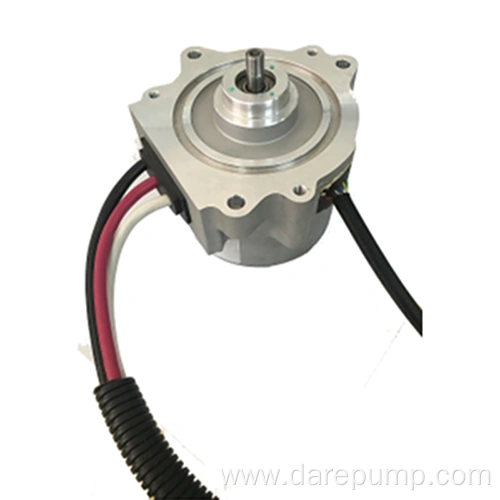
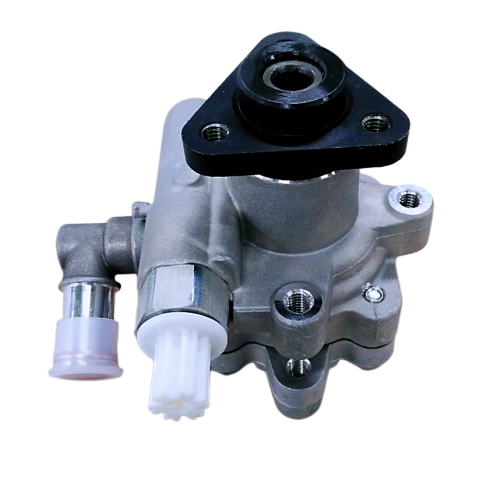
Product Details

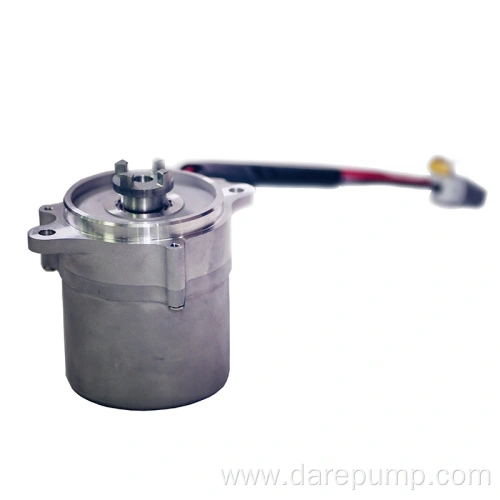
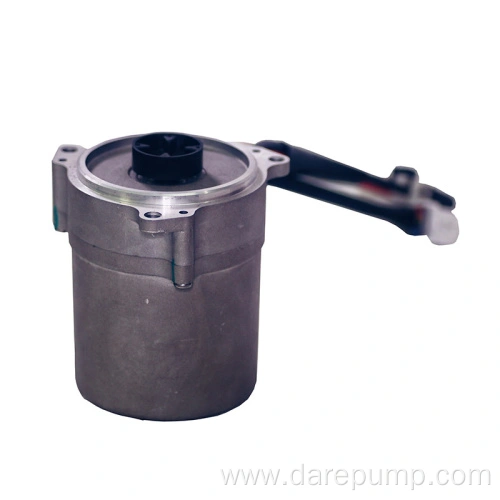
Durable power steering pump
Subcategory
Keywords
- Description
-
Product Attributes
Product Model: FZB30A27A
Product Brand: FZB
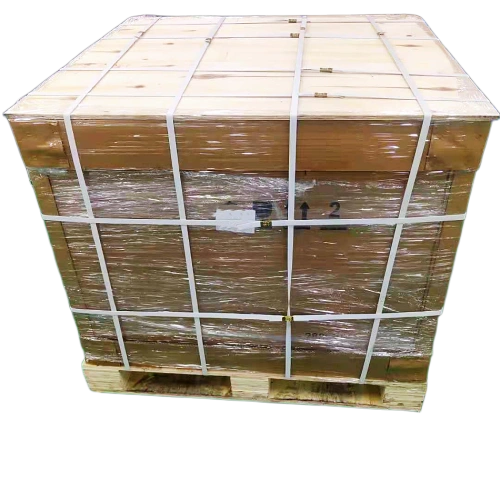
Product Origin: ChinaPackaging and Delivery
Sales Unit: Piece
Packaging Type: Paper Box, PalletDescription
How does the power steering pump work?
The vane pump generally consists of a pump body with an inner cavity of double arc curves, a slotted rotor, and vanes. Some are mounted on the flywheel housing at the rear end of the engine and are also driven by the timing gear. When the engine is running, it drives the rotor of the booster pump to rotate, and the vanes move outward along the vane slots under the action of centrifugal force, close to the inner wall of the pump body. During the rotation of the rotor, the enclosed volume between the vanes continuously increases and decreases, achieving the process of oil suction and oil pressure. Each rotation of the rotor completes two cycles of oil suction and oil pressure. There is also a safety valve in the pump body to limit the maximum pressure. When the external load of the steering system increases, causing the oil pressure to rise to a certain value, the safety valve opens to unload the load. A throttle valve and a flow control valve are also installed in the pump body to ensure that the displacement of the booster pump remains basically stable.
Key ParametersProduct Name Hydraulic Power Steering Pump Product Function Provide hydraulic oil for the steering gear Pump Model Vane Pump Product Number FZB30A27A REF. PN 52112196 OEM PN 52195349, 52209905 Product Application Fiat Displacement 6.88 ml/r Maximum Pressure 7.78~8.78 Mpa Speed Range 550-7000 r/min Flow Rate 5.3~6.8 L/min Inlet φ15.9 mm Outlet M16×1.5 Rotation Direction Right Heavy Guidance
1. Fault Symptoms. Vehicles equipped with power steering should be very light, but feel difficult and heavy to steer during driving.
2. Fault Causes. The oil reservoir is low on oil or the oil level is below the specified requirement; poor sealing at various oil pipe joints, leading to leaks; air has entered the steering hydraulic circuit; deformed or blocked oil pipes; insufficient tension in the power steering pump drive belt, causing slippage; severe internal wear or leakage in the power steering pump, resulting in substandard oil pump output pressure; failure of the pressure regulating valve inside the power steering pump, leading to low output pressure; internal leakage in the steering control valve or power cylinder; damage or improper adjustment of the mechanical steering system.
3. Fault Diagnosis. When heavy steering occurs, the following methods can be used for diagnosis:
(a) Check if the tire pressure is normal and inflate to the specified pressure.
(b) Check for leaks at the joints of the steering hydraulic system, and inspect the oil pipes for damage, deformation, or cracking. If defects are found in the oil pipes, they should be replaced in a timely manner; if there are leaks at the oil pipe joints, they should be tightened, and if necessary, the oil pipes should be replaced and reconnected.
(c) Check the tension of the power steering pump drive belt to see if it is slipping or damaged. If problems are found, adjust the tension of the drive belt or replace it with a new one as specified.
(d) Measure the output oil pressure of the power steering pump to identify the faulty component. Before testing, connect a pressure gauge (with a valve) that matches the specified oil pressure between the pressure output port of the power steering pump and the pressure input pipe of the steering control valve. During the test, open the pressure gauge valve fully, start the engine at idle, and turn the steering wheel to the left or right limit to measure the output oil pressure of the steering pump. If the oil pressure does not reach the factory specified pressure, and the oil pressure does not rise when gradually closing the pressure gauge valve, it indicates a fault in the power steering pump; if the oil pressure does not reach the factory specified value, but there is a rising trend in oil pressure when the pressure gauge valve is gradually closed, and the oil pressure can reach the specified value, it indicates that the power steering pump is in good condition, and the fault lies in the steering control valve or power cylinder; if the oil pressure is normal during the test, the fault lies in the mechanical steering system.
(e) Check the mechanical steering system. Rotate the steering wheel and check if the components related to the steering column shaft rotate smoothly; check if the steering universal joints and ball joint connections of each drive rod are too tight; check if the thrust bearing of the steering joint is low on oil or damaged. If problems are found, adjust or replace and reinstall; if all the above checks are normal, the fault lies in the steering gear. Check the gear rack steering gear, adjust the clamping force of the rack top block to ensure that the lateral gap between the rack and the gear is appropriate, allowing the rack to move freely. Replace any bent frames.
Related Products
Product Consulting
* Note: Please be sure to fill in the information accurately and keep the communication unblocked. We will contact you as soon as possible