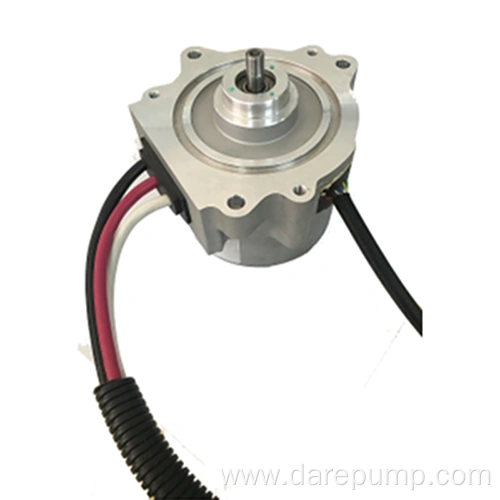
Product Details

Lubrication Oil Pump for Transmission CHERY
Subcategory
Keywords
- Description
-
Product Attributes
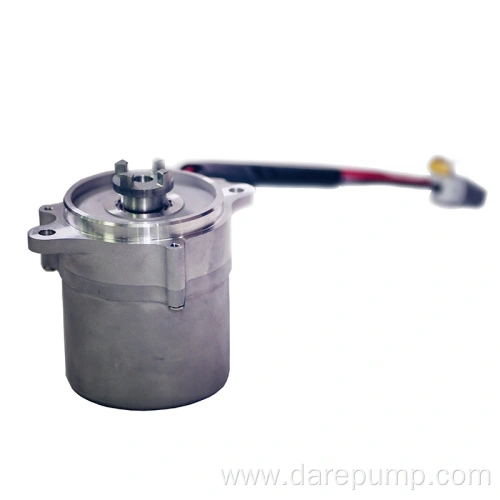
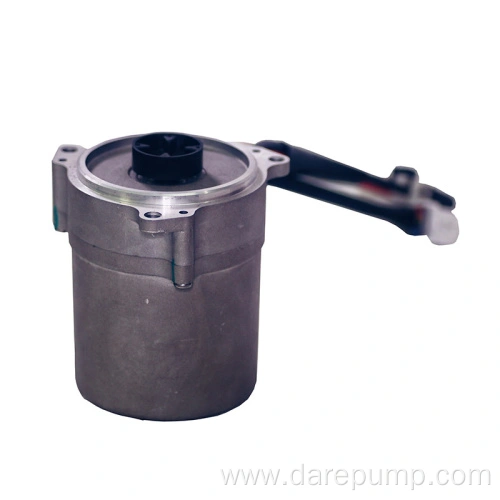
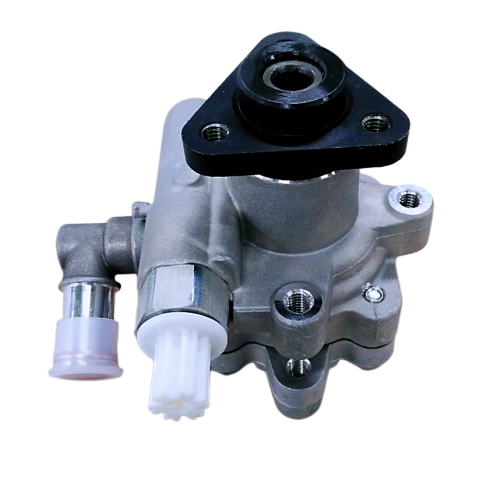
Model No.:FBB93
Brand:FZB
Place Of Origin:China
Type:External Gearing
Application:HEV, NEVPackaging & Distribution
Selling Units:Piece/Pieces
Package Type:PAPER BOX, PALLETProduct Description
Mechanical oil pump
Currently, most traditional automatic transmissions use mechanical oil pumps, such as the Volkswagen DQ380 transmission. The power of the mechanical oil pump comes from the engine. As long as the engine is running, the automatic Transmission Oil Pump is in operation and outputs pressure oil.
The mechanical oil pump of an automatic transmission is generally installed at the front or rear end of the automatic transmission, generally driven by gears, and partially driven by chains.
In addition, currently, mechanical oil pumps for gearboxes generally use constant displacement oil pumps, with a few using variable displacement oil pumps.
Critical parametersPart Name Transmission Oil Pump Function Lubrication DARE PN FBB93 Application HEV, NEV Type of Pump External Gearing Max. Pressure 2bar Speed Range 500-6000r/min Flow Rate 20L/min Working Temperature -40 to 120℃ Cycloidal rotor pump
It is a special type of internal Gear Pump with teeth, which has the advantages of simple structure, small volume, low noise, stable operation, and good high-speed performance. Its disadvantages are large flow pulsation and high machining accuracy. It consists of a pair of internally meshed rotors, pump casings, and chambers whose volume varies with the rotation of the rotor. When the rotor rotates clockwise, the volume of the working chamber on the right side of the center line of the inner and outer rotors changes from small to large, forming a vacuum oil suction. The volume of each working chamber on the left side of the center line changes from large to small, and the hydraulic pressure is extracted. The cycloidal rotor pump consists of a pump casing, a pump cover, and a pair of internally engaged rotors, as shown in the figure. The inner rotor is an outer gear with an epicycloid tooth profile curve, while the outer rotor is an inner gear with an arc tooth profile curve. The rotation centers of the inner rotor and the outer rotor are different, and there is an eccentric distance E between them. Generally, the number of teeth of the inner rotor can be 4, 6, 8, 10, etc. The outer rotor has one more tooth than the inner rotor. The more teeth in the inner rotor, the smaller the oil pulsation. The internal rotor commonly used in automatic transmissions has 10 teeth. When the engine is running, the inner and outer rotors of the belt driven oil pump rotate in the same direction. The inner rotor is a driving gear, and the outer rotor rotates one tooth slower than the inner rotor. As the rotor rotates, the volume of the working chamber continuously changes. When the rotor rotates clockwise, the volume of the working chamber on the right side of the center line of the inner and outer rotors changes from small to large, forming a local vacuum. Hydraulic oil is sucked in from the oil suction port, and the volume of the working chamber on the left side of the center line of the inner and outer rotors changes from large to small. Hydraulic oil is discharged from the oil outlet.
Related Products
Product Consulting
* Note: Please be sure to fill in the information accurately and keep the communication unblocked. We will contact you as soon as possible